症状性腰椎间盘突出症(LDH)是引起腰痛和下肢放射痛的最常见原因。如经过6周的保守治疗后症状仍未缓解时,进行性腰痛和神经功能缺损的患者通常需要手术治疗[1],因为疼痛持续时间过长可能导致治疗的效果差[2]。经皮内镜下腰椎间盘切除术(PELD)的优点包括皮肤切口小(<1 cm)、肌肉损伤轻、恢复快、疗效好[3]。随着椎间孔成形术的发展,小的、移位及游离椎间盘、复发性椎间盘、高髂嵴L5~S1椎间盘突出都可以通过PELD解决[3]。大多数PELD手术的平均住院时间为2~5天,近期有报道,PELD可以作为日间手术治疗椎间盘突出症以解决成本问题以及住院紧张[4,5],效果良好。本研究的目的是评估和比较日间行腰椎间盘突出症PELD手术的患者和住院患者的临床效果和麻醉选择。
1 研究对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
本研究为回顾性研究,所有数据均来源于广州市增城区人民医院病案室,病例资料完整。2016年8月至2018年10月共有153名患者住院接受PELD手术,(入院手术组),217名患者接受PELD手术后当日出院(日间手术组)。患者接受磁共振神经成像(MRN)或磁共振成像(MRI)和计算机断层扫描(CT)检查确定LDH诊断,所有患者在研究开始时签署了知情同意书。
入组标准:①单节段LDH,经CT和MRI证实,并有相应症状和体征,或者伴其他阶段LDH,轻度且无症状;②经过6周以上保守治疗失败,多次发作。排除标准:①多节段LDH;②不稳定LDH及伴有腰椎滑脱;③复发LDH。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 麻醉选择 通常情况下,我们会优先考虑局麻或者硬膜外麻醉。全麻使用于对于术中不能配合的、L5/S1高髂嵴的LDH患者;也适合于由于术中疼痛不可耐受,不得不停止手术患者。
1.2.2 手术方法 所有手术均由具有10年以上的脊柱外科医生完成。按照标准经皮内窥镜脊柱系统(TESSYS)(5.5,6.5,7.5 mm,Joimax系统)进行以下手术:患者取俯卧位,C臂X光机透视下定位腰椎间隙,并在患侧皮肤上标记进针点,用碘伏消毒术野,常规铺无菌巾。利多卡因、罗哌卡因在穿刺点作局麻,C臂X光机透视引导下行腰患侧椎间孔穿刺,在穿刺针到达腰患侧小关节突上前缘时,插入导丝,拔出穿刺针,在进针点作长约1.0 cm的切口,在导丝引导下用软组织扩张器扩张软组织通道,用骨钻扩张椎间孔,置入工作通道,连接椎间孔镜到光源和成像系统,用髓核钳清除软组织,并用蓝剪分离黄韧带及突出髓核周围组织,将突出髓核摘除,见腰患侧神经根已松驰,确定无活动性出血,清点器械无误后注入得宝松一支,拔除椎间孔镜及工作套筒,缝合皮肤。
术后VAS评分低于3分者于术后3~6小时出院,给予注射地塞米松5 mg及NSAIDs出院带药作为对症治疗,患者带腰围下床,卧床休息4周,在此期间,做背部和腹部肌肉锻炼。
1.2.3 数据收集和随访 记录和分析入院期间、门诊复诊及通过电话随访的临床数据,包括:①手术时间、住院时间、费用、术后并发症、延迟出院和再入院的发生率及原因;②VAS评估腿部疼痛程度和背部疼痛;③术后6月Oswestry功能障碍指数(ODI)(0~100%)评估功能状态;④根据Mac-Nab标准(优秀、良好、公平、差)评定手术效果。
1.3 数据分析
收集的数据用SPSS 22.0统计软件进行分析。定量数据以均数±标准差表示,定性数据以频度(%)表示。分析数据的正态性,组间采用Mann-Whitney U检验,用Wilcoxon试验对两组进行数据分析,组间定性数据行χ2检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 两组患者一般情况手术完成情况
纳入标准的研究对象中,153例为住院接受PELD手术,入院时间2~6天;实施日间手术217例,入院时间3.6~8 h。两组在性别、年龄、手术水平、手术时间等方面无显著性差异,日间手术组总费用低于入院手术组。所有患者均顺利完成PELD,术中无患者出现大出血和术中血管损伤,无患者中转为开放手术。日间手术组中3例由于术中疼痛改为硬膜外麻醉,1例改为全麻;入院手术组1例局麻改为硬膜外麻醉,3例改为全麻,为发生麻醉并发症。两组基本特征见表1。
表1 两组接受PELD患者的基本情况
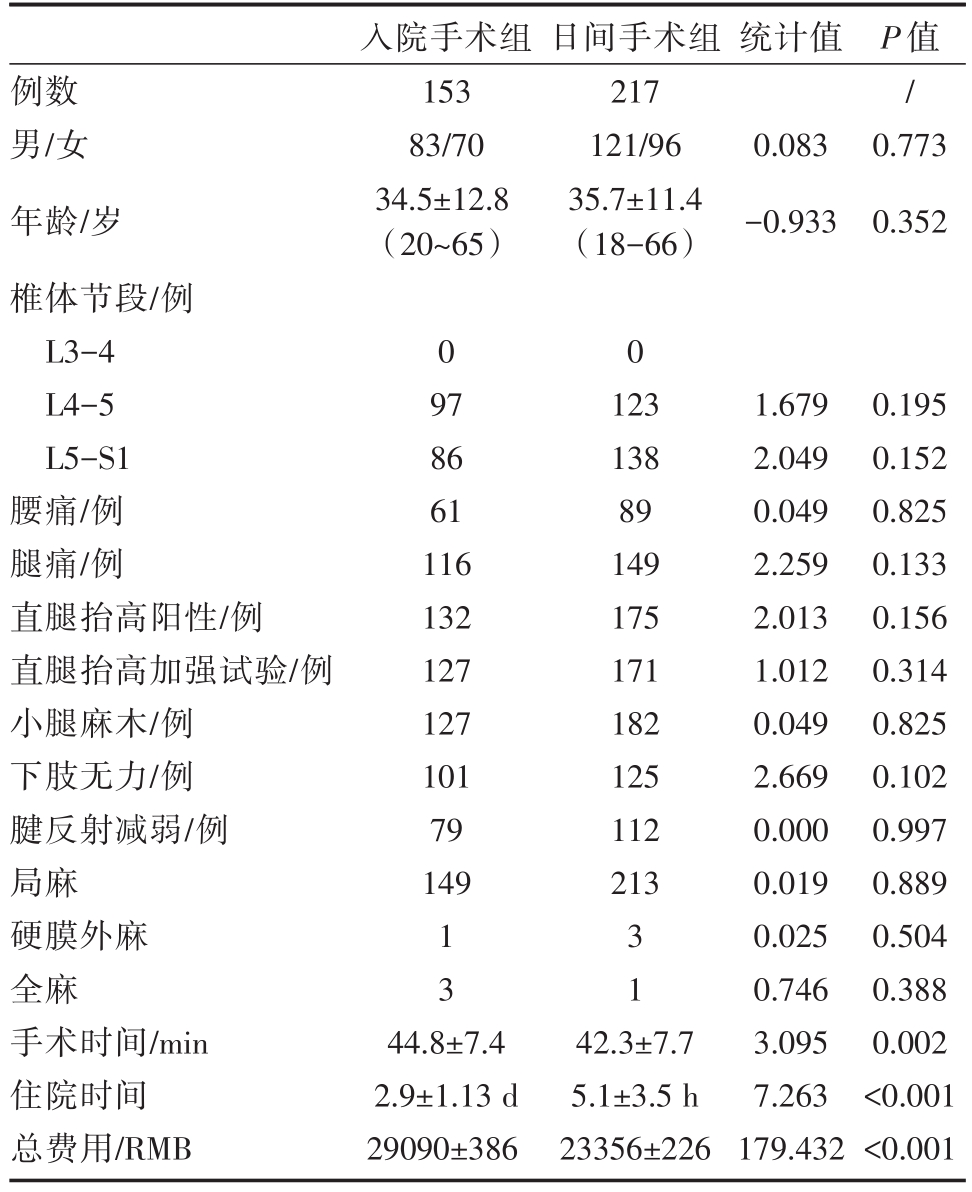
统计值例数男/女年龄/岁椎体节段/例L3-4 L4-5 L5-S1腰痛/例腿痛/例直腿抬高阳性/例直腿抬高加强试验/例小腿麻木/例下肢无力/例腱反射减弱/例局麻硬膜外麻全麻手术时间/min住院时间总费用/RMB入院手术组153 83/70 34.5±12.8(20~65)日间手术组217 121/96 35.7±11.4(18-66)0.083-0.933 P值/0.773 0.352 0 0 97 86 61 116 132 127 127 101 79 149 123 138 89 149 175 171 182 125 112 213 1 3 3 1 44.8±7.4 2.9±1.13 d 29090±386 42.3±7.7 5.1±3.5 h 23356±226 1.679 2.049 0.049 2.259 2.013 1.012 0.049 2.669 0.000 0.019 0.025 0.746 3.095 7.263 179.432 0.195 0.152 0.825 0.133 0.156 0.314 0.825 0.102 0.997 0.889 0.504 0.388 0.002<0.001<0.001
2.2 两组患者术后不良反应及并发症
日间手术组术后当日出院198例,延迟出院19例,其中6例患者处于心理因素主动要求继续留院;入院手术组13例延迟出院,其原因见表2。日间手术组12例(5.53%)出现手术并发症;入院手术组则有12例(7.84%)。主要为日间手术组和入院手术组分别有7例和5例出现术后感觉障碍,口服甲钴胺或功能锻炼等保守治疗3个月后逐渐恢复;日间手术组有1例、入院手术组2例出现术后暂时性运动障碍,表现为足趾无力或足下垂(表2)。恶心、呕吐、头痛、硬脊膜撕裂的患者均被建议留院观察治疗效果。两组并发症发生率无显著性差异(P=0.23)。
表2 两组患者并发症及推迟出院分析(例/%)

例数硬脊膜撕裂感觉迟钝神经功能缺损恶心/呕吐头痛心理因素入院手术组13(8.50%)2(1.30%)5(3.30%)2(1.30%)1(0.65%)2(1.3%)-日间手术组19(8.80%)1(0.46%)7(3.22%)1(0.46%)1(0.46%)2(0.92%)6(2.80%)统计值0.008 0.093 0.076 0.093-0.025-P值0.930 0.760 0.783 0.760-0.875-
2.3 再入院分析
日间手术组有26例失访,入院手术组13例失访。日间手术组术后有12例、入院手术组有9例术后6月内再次入院,两组再入院率无显著性差异(P=0.885)。再入院主要原因是复发性椎间盘突出、髓核游离和神经痛(表3),MRI检查发现椎间盘组织残留。复发患者再次进行手术后痊愈。
表3 两组患者再入院分析(例/%)
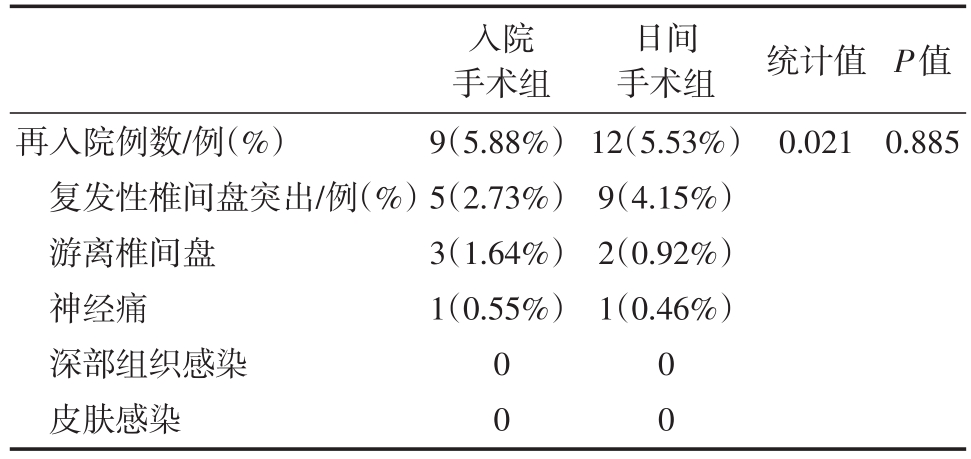
再入院例数/例(%)复发性椎间盘突出/例(%)游离椎间盘神经痛深部组织感染皮肤感染入院手术组9(5.88%)5(2.73%)3(1.64%)1(0.55%)日间手术组12(5.53%)9(4.15%)2(0.92%)1(0.46%)统计值0.021 P值0.885 0 0 0 0
2.4 6月随访评价
根据Mac-Nab标准,术后6月的手术结果如下:①日间手术组217例,其中优109例、良98例、可4例、差6例;②入院手术组153例,其中优71例、良70例、可7例、差5例,两组间差异无统计学意义(P=0.457,Fisher精确检验)。日间手术组和入院手术组的满意率分别为84.2%和85.8%,两组间差异无统计学意义(P=0.43)。从手术后到随访6月,两组背痛和腰育VAS评分和ODI评分术前术后均明显改善(P均<0.001),组间对比差异无统计学意义。(表4)。
表4 两组VAS-B、VAS-L、ODI评分比较
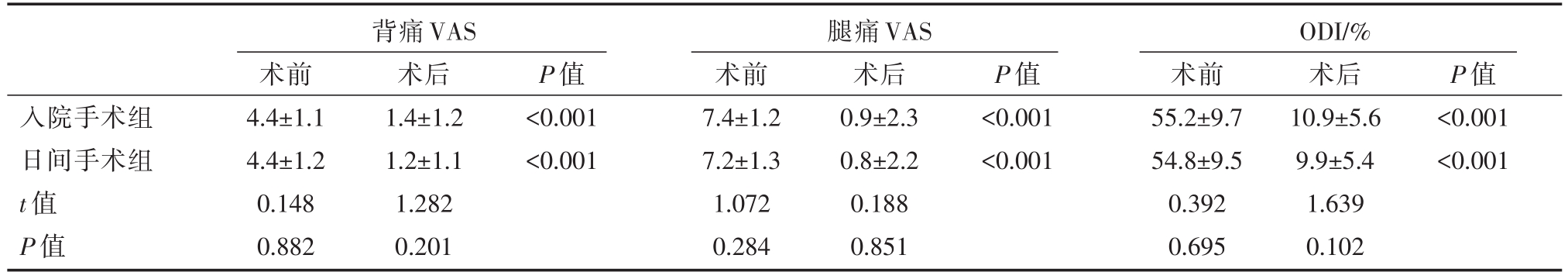
背痛VAS 腿痛VAS ODI/%入院手术组日间手术组t值P值术前4.4±1.1 4.4±1.2 0.148 0.882术后1.4±1.2 1.2±1.1 1.282 0.201 P值<0.001<0.001术前7.4±1.2 7.2±1.3 1.072 0.284术后0.9±2.3 0.8±2.2 0.188 0.851 P值<0.001<0.001术前55.2±9.7 54.8±9.5 0.392 0.695术后10.9±5.6 9.9±5.4 1.639 0.102 P值<0.001<0.001
3 讨论
日间手术是指允许患者在同一工作日出院的手术,采用住院的程序但非门诊手术流程。日间手术具有手术时间短、感染风险低、恢复快、费用低等优点,越来越受到临床医生和患者的青睐[6,7]。对于病人来说,日间手术可以减少等待时间和住院时间,花更少的钱去做同样的手术。在社会医疗资源有限的情况下,日间手术可以提高患者周转率,缩短病床天数,减轻保险负担。很多临床研究报告显示,日间手术的优势也可减少院内感染,术后可很快恢复正常生活并减少家属的麻烦。de′Angelis等[8]报道 24 例肝脏良性肿瘤采用微创腹腔镜切除术(切除范围不超过两个肝段),其中23例患者在24小时内出院。中位手术时间90分钟,中位气腹时间60分钟,估计失血量50毫升,无需输血,未发生麻醉相关并发症。作者认为,只要患者出院后有良好的成年人照顾,护理者(或陪护人员)了解手术过程、潜在的并发症以及提前出院所需的条件,因此,日间手术的执行可能成为一种趋势。
传统的开放式手术一直是治疗LDH的选择,然而,许多缺点和不良反应降低手术本身的效果,如传统的腰椎手术造成的软组织损伤太大,医疗费用高。随着微创技术和相关设备的发展,LDH的研究取得了显著进展。与开放手术相比,PELD只需要<10 mm的皮肤切口。由于使用了局部麻醉,患者和外科医生可以在手术过程中进行沟通,以方便确认疗效。此外,手术后症状可以立即缓解。因此,日间手术是可行的。然而,大多数已发表的关于PELD的研究仍然显示平均住院时间为2~5 天[9,10],患者需要住院,这可能增加了医院感染的风险。但LDH手术对麻醉要求较高,PELD可在局麻、全麻或硬膜外麻醉下进行。局麻手术术中的疼痛可能影响手术过程,全麻或硬膜外麻醉有效的控制术中疼痛,但可能有更大的神经并发症风险,使患者无法配合手术[11,12]。本组病例在手术过程中,尽管局麻手术患者不多,但总体对疼痛的耐受性良好,只是在暴露黄韧带,神经根牵拉时,暴露及除椎间盘纤维环时,提示局麻下行PELD的患者有不同程度的VAS症状轻微疼痛。作者体会,局麻下行PELD需要经验丰富的医生来操作以达到上述要求。
日间手术和非日间手术比较的结果,两组患者的疼痛和功能参数均有显著的临床改善。术后6月的随访显示,日间PELD组的VAS和ODI评分与住院PELD组相当,两组的手术满意度与文献报道相当[13,14]。基于这些结果,PELD的日间手术在治疗LDH方面可以达到与PELD需要住院治疗的同等效果。本组病例中,日间手术和非日间手术的并发症发生率分别为8.20%和5.36%,与报道的结果相似[15]。这些因素可能导致延迟出院,其中术后感觉障碍是主要的手术并发症。住院PELD手术组共有7例术后感觉障碍,日间手术组有8例术后发生感觉障碍。射频凝固器向神经结构的热传导是术后感觉障碍的主要原因,硬膜外腔插管对背根神经节的机械压迫可能是感觉障碍的另一个原因[16,17]。Choi等[17]总结 67 例 PELD,2 例硬脊膜损伤导致脑脊液漏,2例神经根损伤及腿部有感觉减退。脑脊液漏无需开放性修复,需要住院观察后好转出院。9例(12%)术后短暂的感觉障碍,并在1个月后逐渐得到改善,MRI显示5例椎间盘残留,其中1例因游离碎片移到对侧,第二天产生坐骨神经痛,另1例椎间盘残留患者症状改善。
患者PELD术后可能出现较重的腿部疼痛、头痛、恶心、胸闷、硬脑膜撕裂或其他并发症。腰背部的疼痛、腹痛(如腹膜后血肿)、术中损伤血管以及术后膀胱和/或直肠功能障碍可能需留院观察,导致延迟出院。PELD术后再入院的主要原因是LDH复发。日间手术和非日间手术的复发率分别为4.15%和2.73%,差异无显著性(P=0.662)。椎间盘突出症的一些复发可归因于负重活动手术后1个月内。在我们的研究中,没有病人在日间手术后出现感染。日间手术和非日间手术的效果相近,住院时间与手术结果无关,而影响手术结果的主要因素可能与操作者的操作有关。本研究的不足之处在于收集样本量有限,并发症或不良反应案例数量过少。另外,由于家庭文化和患者心理因素,部分患者选择延迟术后出院,可能影响了数据的真实性。患者的疼痛评估可能不太准确。
总之,腰椎间盘突出症PELD作为日间手术与非日间手术具有相同的安全性和有效性,同时显著降低了患者的平均住院时间和住院费用。此外,它使医院能够更有效地利用有限的卫生资源。
参考文献
[1] Peul WC,van Houwelingen HC,van den Hout WB,et al.Surgery versus prolonged conservative treatment for sciatica[J].N Engl J Med,2007,356(22):2245-2256.
[2] Sabnis AB,Diwan AD.The timing of surgery in lumbar disc prolapse:A systematic review[J].Indian J Orthop,2014,48(2):127-135.
[3] Price JP,Dawson JM,Schwender JD,et al.Clinical and radiologic comparison of minimally invasive surgery with traditional open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion:a review of 452 patients from a single center[J].Clin Spine Surg,2018,31(2):E121-E126.
[4] Lewandrowski KU.Incidence,Management,and cost of complications after transforaminal endoscopic decompression surgery for lumbar foraminal and lateral recess stenosis:a value proposition for outpatient ambulatory surgery[J].Int J Spine Surg,2019,13(1):53-67.
[5] Cao J,Huang W,Wu T,et al.Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for lumbar disc herniation as day surgery-shortterm clinical results of 235 consecutive cases[J].Medicine(Baltimore),2019,98(49):e18064.
[6] Jiang H,Han J,Lu A,Liu X.Day surgery management model in china:practical experience and initial evaluation[J].Int J Clin Exp Med,2014,7(11):4471-4474.
[7] Pivot D,Hoch G,Astruc K,et al.A systematic review of surgical site infections following day surgery:a frequentist and a Bayesian meta-analysis of prevalence[J].J Hosp Infect,2019,101(2):196-209.
[8] de"Angelis N,Menahem B,Compagnon P,et al.Minor laparoscopic liver resection:toward 1-day surgery?[J].Surg Endosc,2017,31(11):4458-4465.
[9] Lin GX,Huang P,Kotheeranurak V,et al.A Systematic Review of Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Spinal Surgery:Preliminary Clinical Results and Complications[J].World Neurosurg,2019,125:425-432.
[10] Patil A,Chugh A,Gotecha S,et al.Microendoscopic discectomy for lumbar disc herniations[J].J Craniovertebr Junction Spine,2018,9(3):156-162.
[11] Fang G,Ding Z,Song Z.Comparison of the Effects of Epidural Anesthesia and Local Anesthesia in Lumbar Transforaminal Endoscopic Surgery[J].Pain Physician,2016,19(7):E1001-1004.
[12] Zhu Y,Zhao Y,Fan G,et al.Comparison of 3 Anesthetic Methods for Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Discectomy:A Prospective Study[J].Pain Physician,2018,21(4):E347-E353.
[13] Kambin P,NASS.Arthroscopic microdiscectomy[J].Spine J,2003,3(3 Suppl):60S-64S.
[14] Ahn Y,Lee U,Kim WK,Keum HJ.Five-year outcomes and predictive factors of transforaminal full-endoscopic lumbar discectomy[J].Medicine(Baltimore),2018,97(48):e13454.
[15] Yao Y,Zhang H,Wu J,et al.Comparison of Three Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery Methods for Revision Surgery for Recurrent Herniation After Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy[J].World Neurosurg,2017,100:641-647.e1.
[16] Choi G,Lee SH,Raiturker PP,et al.Percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy for intracanalicular disc herniations at L5-S1 using a rigid working channel endoscope[J].Neurosurgery,2006,58(1 Suppl):ONS59-68.
[17] Choi G,Lee SH,Raiturker PP,et al.Percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy for intracanalicular disc herniations at L5-S1 using a rigid working channel endoscope[J].Neurosurgery,2006,58(1 Suppl):ONS59-68.

